Introduction
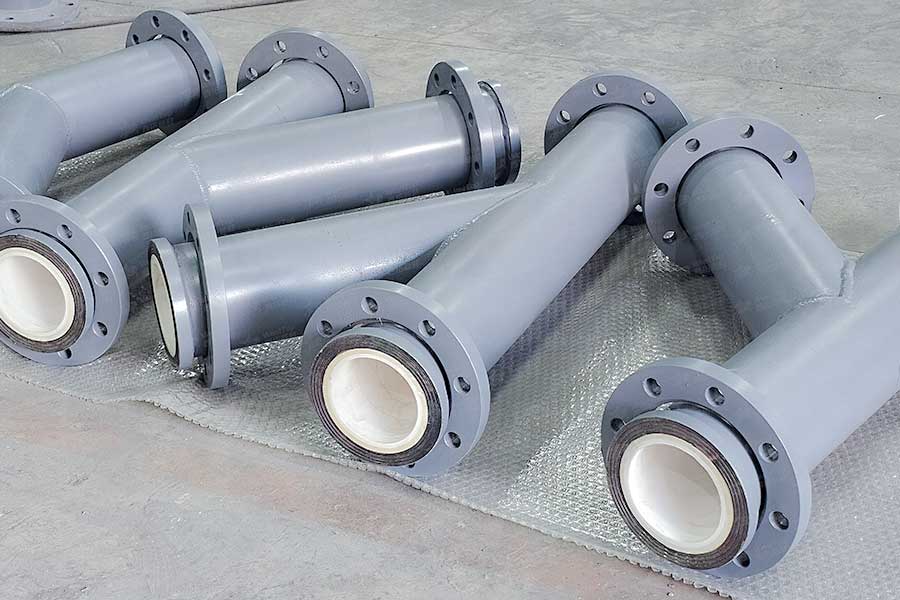
In industrial operations, transporting high-hardness materials such as fly ash, mineral powder, and steel slag often causes severe wear in ordinary steel pipes, leading to frequent replacements and high maintenance costs. In contrast, wear-resistant ceramic pipes have become the preferred choice in power plants, metallurgy, and mining industries due to their exceptional wear resistance and long service life. This article explores the advantages of wear-resistant ceramic pipes in terms of material composition, wear coefficient, application scenarios, and comparison with conventional pipes.
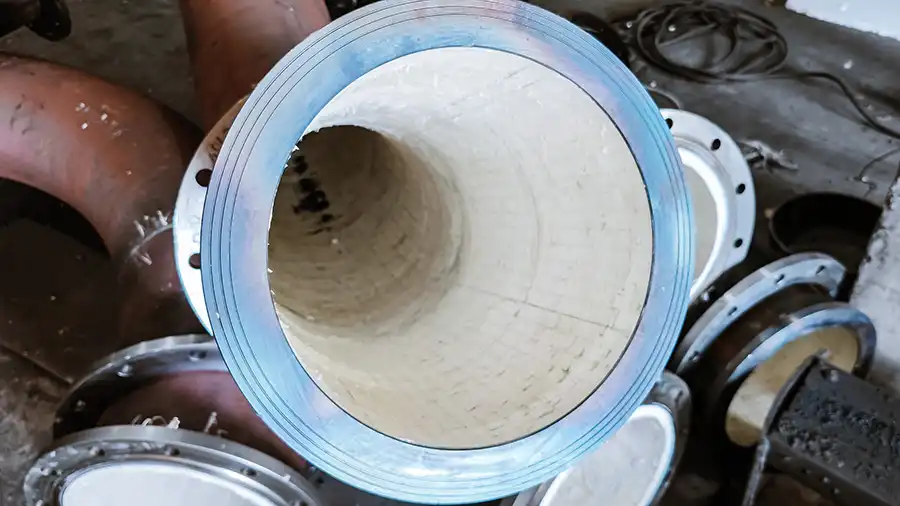

1. Material Composition of Wear-Resistant Ceramic Pipes
Wear-resistant ceramic pipes typically use alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramics as the inner lining, with alumina content usually above 92%. High-end products can even reach 95–99%.
Hardness of alumina ceramics: HRA 85+ (close to corundum, second only to diamond)
Bonding method: Fixed to the steel pipe inner wall through adhesive, welding, or self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS), ensuring stability under high-impact and severe wear conditions
2. Wear Coefficient and Service Life Comparison
Studies show that wear-resistant ceramic pipes have 10 times the wear resistance of ordinary steel pipes and also outperform high-manganese steel and cast stone pipes.
| Pipe Type | Lifespan |
| Ordinary steel pipe | 6–12 months |
| Heat-resistant alloy steel pipe | 12–18 months |
| Wear-resistant ceramic pipe | 3–7 years |
3. Application Scenarios of Wear-Resistant Ceramic Pipes
Wear-resistant ceramic pipes are widely used in:
- Power plants: Fly ash transportation, dust removal pipelines
- Steel industry: Blast furnace coal injection, mineral powder recovery
- Mining: Long-distance slurry and tailings pipelines
- Cement plants: Cyclone separators, powder selection pipelines
4. Comparison with Conventional Pipes
| Pipe Type | Hardness (HRA) | Lifespan | Cost | Overall Value |
| Ordinary steel pipe | HRA 40–45 | 6–12 months | Low | Low |
| High-manganese steel pipe | HRA 55–60 | 1–2 years | Medium | Medium |
| Cast stone pipe | HRA 70+ | 2–3 years | Medium | Medium |
| Wear-resistant ceramic pipe | HRA 85+ | 3–7 years | Medium-High | High |
Although wear-resistant ceramic pipes have a higher initial cost, their long service life and lower maintenance costs make the overall cost-performance ratio much better.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the typical lifespan of wear-resistant ceramic pipes?
In standard fly ash transport environments, the lifespan can reach 5–7 years; in high-impact slurry environments, it remains above 3 years.
2. Why is there a big price difference for wear-resistant ceramic pipes?
Prices depend on alumina content, production process, and manufacturer quality standards. Pipes with higher alumina content and denser sintering are more expensive but last longer.
3. How to choose a reliable ceramic pipe manufacturer?
Select manufacturers with official testing reports, lifespan comparison data, and large-scale project cases, avoiding low-cost, low-quality products.
Conclusion
Through an analysis of material composition, wear coefficient, application scenarios, and comparison with conventional pipes, it is evident that wear-resistant ceramic pipes far exceed traditional pipes in lifespan and overall performance. While the initial investment may be slightly higher, the long-term cost benefits make them the ideal choice for power plants, steel mills, and mining industries.