Ⅰ. Technical challenges of industrial equipment wear and tear
In the industrial production system, the wear of equipment surface is a technical problem that restricts the development of industrial enterprises for a long time. The rapid loss of material surface not only leads to the decrease of equipment operation efficiency and the increase of maintenance cost, but also may lead to structural failure, resulting in early scrapping of equipment, which has a great economic impact on enterprises. In this context, as a typical representative of alumina-based functional materials, wear-resistant ceramics have become a key technical solution to solve industrial wear problems due to their excellent comprehensive properties.

Ⅱ.The core performance advantages of wear-resistant ceramic materials
( 1 ) Excellent wear resistance
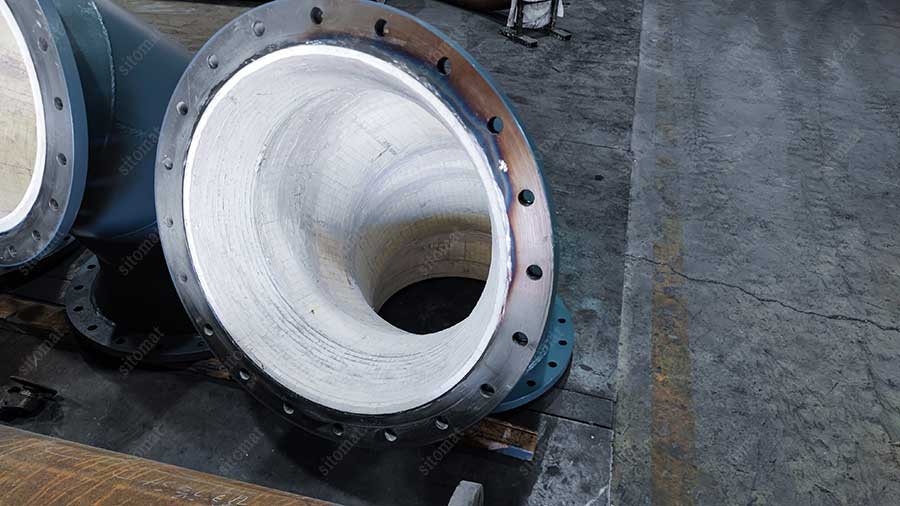
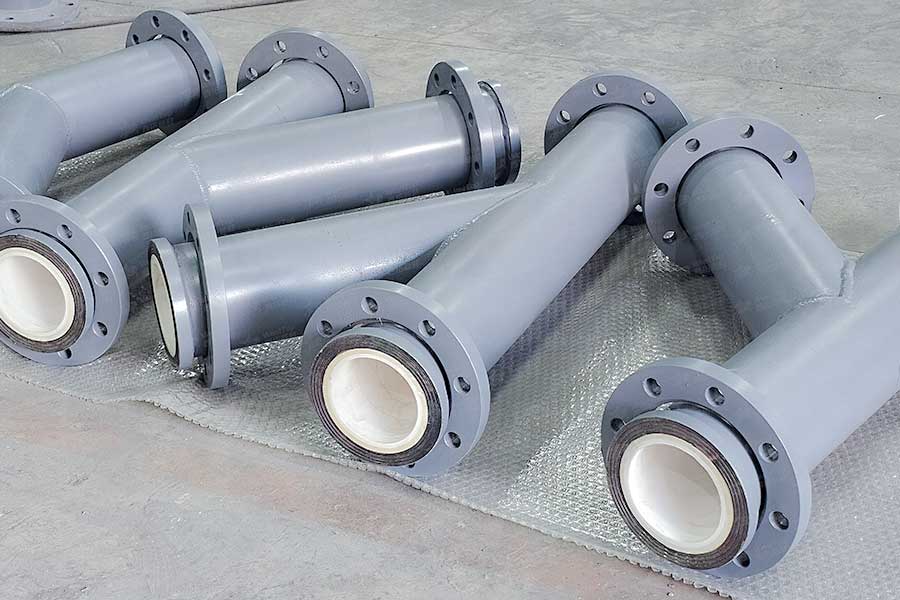
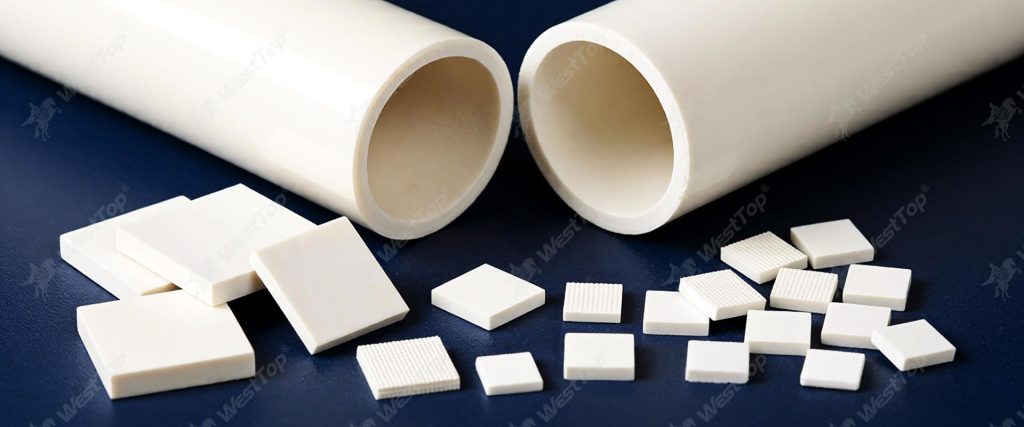
The technical advantages of wear-resistant ceramic materials are first reflected in their outstanding wear resistance. The material system mainly includes a series of products such as wear-resistant ceramic lining, alumina ceramic lining brick, rubber composite wear-resistant ceramic, ceramic lining composite pipe, etc., which can achieve efficient wear-resistant protection in multiple industrial scenarios. Its crystal structure endows the surface of the material with extremely high hardness, and the Vickers hardness can reach 1500-1800 HV, which can effectively resist various wear forms such as solid particle erosion and fluid abrasion. In high-speed operating mechanical systems ( such as fan impellers, pump body components ) and harsh working conditions with strong abrasive particles, wear-resistant ceramics exhibit stable performance and significantly reduce the surface wear rate of the equipment.
( 2 ) Outstanding corrosion resistance
In view of the special working conditions in the fields of chemical industry and metallurgy, wear-resistant ceramics show excellent chemical stability. Its main component α-Al2O3 has very low chemical activity, and its corrosion rate is very low in corrosive media such as acid, alkali and salt, which is significantly better than that of ordinary metals and polymer materials. This feature enables it to achieve long-term reliable protection in scenarios such as pipeline systems that contact corrosive fluids, and reaction vessel linings.
Ⅲ.Engineering convenience of material application
The engineering application of wear-resistant ceramics has technical economy. Through precision forming and CNC machining technology, customized preparation can be carried out according to the geometric characteristics of the equipment components to form the best matching structure with the matrix. The installation process adopts mature technical solutions such as high-strength adhesive bonding and mechanical inlaying, which does not require special tooling equipment and significantly shortens the equipment maintenance cycle. The field measured data show that compared with the traditional surfacing wear-resistant layer process, the installation time of wear-resistant ceramics can be reduced by 60 % -70 %, which effectively improves the operation and maintenance efficiency of industrial systems.
Ⅳ.Application practice in typical industrial fields
( 1 ) Iron and steel metallurgy industry
In the process of iron and steel production, wear-resistant ceramics are mainly used in the inner and outer surface protection of loading tanks, spiral conveying pipelines and material transfer equipment. In view of the high-temperature oxide scale erosion scene of the hot rolling production line, the use of alumina ceramic lining technology can prolong the service life of the equipment by 3-5 times, and significantly reduce the frequency of production line shutdown caused by equipment replacement. The measured data of a large steel plant show that the annual equipment maintenance cost decreases by 42 % and the capacity utilization rate increases by 6.5 % after the use of wear-resistant ceramic protection.
( 2 ) Mining industry
The high concentration of abrasive particles in mining conditions puts forward strict requirements on the wear resistance of equipment. Wear-resistant ceramics exhibit excellent abrasive wear resistance in the application of ore crushing equipment ( such as jaw crusher liner ), belt conveyor rollers and hoppers. Compared with traditional high manganese steel materials, the service life of ceramic protective components is increased by 2-3 times, which effectively guarantees the stability of continuous operation in mines and reduces the difficulty of equipment operation and maintenance in open-pit mines and underground mines.
( 3 ) Electric energy industry
In the boiler system of power plant, wear-resistant ceramics are used for anti-corrosion and wear-resistant protection of pulverized coal pipelines, cyclone separators and desulfurization devices. Aiming at the flue gas environment with high temperature ( ≤ 1200 °C ) and high dust concentration ( ≥ 50 g / Nm 3 ), the wear rate of the ceramic lined pipe is only 1 / 10 of that of the ordinary carbon steel pipe. At the same time, it can resist the corrosion of acid gases such as SO 2 and NOx, which significantly improves the reliability of power generation equipment. The application case of a 300 MW coal-fired unit shows that after the ceramic protection is adopted, the average annual pipeline replacement volume decreases by 70 %, and the maintenance cycle is extended to 18 months.
Ⅴ.Technical value and development prospect
As an important branch of high-performance structural ceramics, wear-resistant ceramics provide a systematic solution for industrial equipment protection through material design and process innovation. Its technical advantages are reflected in the organic unity of material performance, engineering adaptability and life cycle cost control, which has become the key material technology to improve the reliability of industrial equipment. With the development of advanced manufacturing technology, the research and development of new technologies such as nano-composite wear-resistant ceramics and gradient functional coatings will further expand the application boundary of the material. In the national strategic areas such as high-end equipment manufacturing and green metallurgy, the engineering application of wear-resistant ceramic materials is expected to usher in a broader development space, providing continuous technical support for the efficient and green operation of industrial systems.