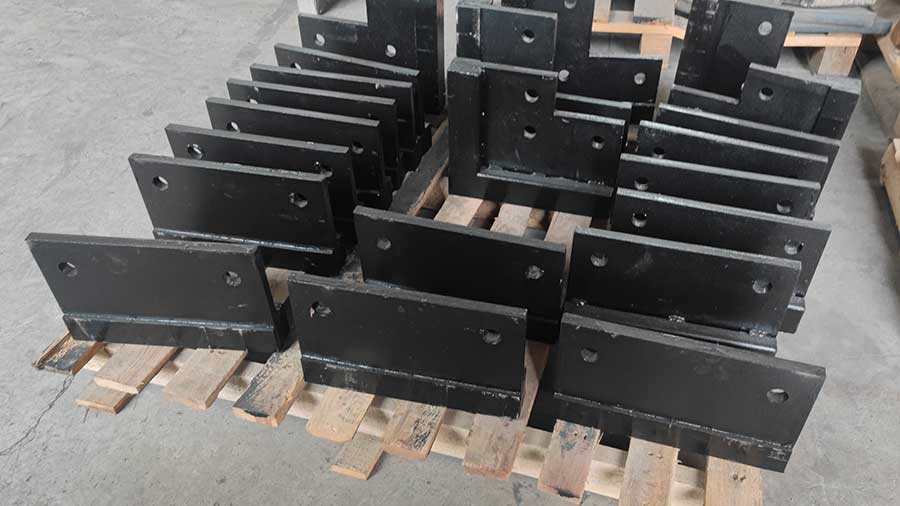
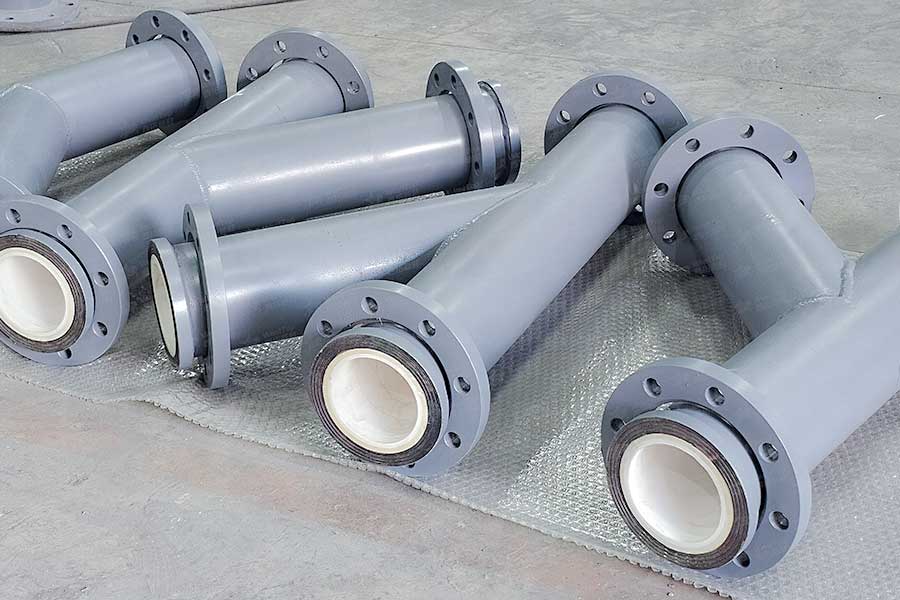
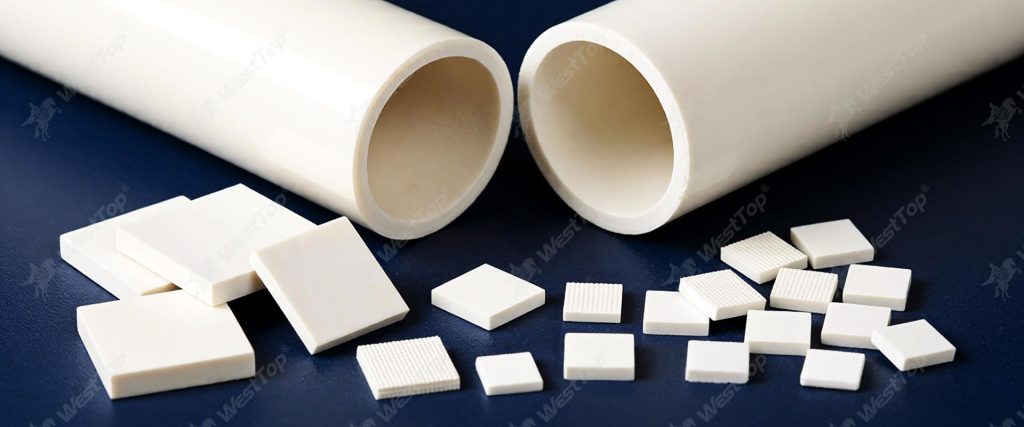
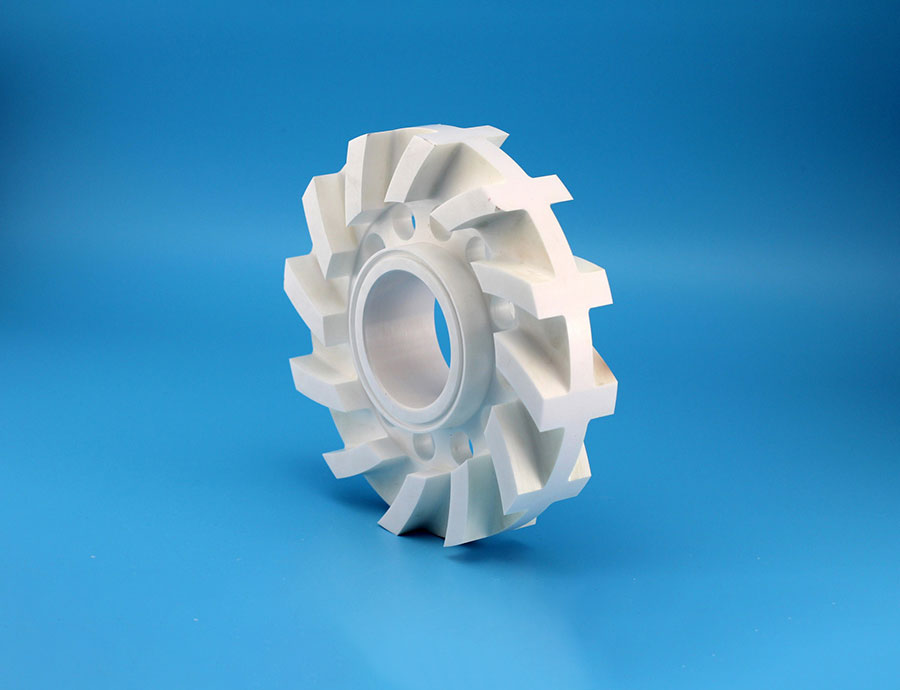
What is cemented carbide
As a kind of alloy material prepared by powder metallurgy process, cemented carbide is mainly composed of metal carbides and bonded metals. It is usually a common collocation of tungsten carbide and cobalt. Cemented carbide has high hardness, high wear resistance, good compressive strength and toughness, excellent corrosion resistance and heat resistance. It can maintain a high hardness level at a temperature of 1000 degrees Celsius, and can maintain a hardness basically unchanged at a temperature of 500 degrees Celsius.

Composition of cemented carbide
Cemented carbide is mainly composed of hard phase and binder phase. The hard phase is the main reason for the hard alloy to become more wear-resistant and harder, it is generally composed of metal carbides that are difficult to melt. Such as common tungsten carbide ( WC ), titanium carbide ( TiC ), tantalum carbide ( TaC ) and so on. These metal carbides have very strong characteristics. They have very high hardness, high melting point, and very stable chemical properties, and are not easy to react with other substances. It is precisely because of these metal carbides, cemented carbide has a particularly good performance. The binder phase is to make the cemented carbide have strong toughness and strength, and will not be easily broken by external force impact. Generally, iron group metals are selected, of which cobalt ( Co ) is used more. The role of cobalt is like glue, which can stick those hard metal carbides tightly together.
How to select the appropriate cemented carbide
Selecting the appropriate cemented carbide requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors. Application scenario is one of the key considerations. If it is used in the field of cutting, it is necessary to accurately select according to the specific properties of the material to be processed, such as hardness, toughness and other indicators, as well as the processing methods used, such as turning and milling. For the application of stamping die, the thickness, hardness and stamping frequency of stamping materials should be fully considered. Secondly, the performance indicators of cemented carbide can not be ignored, including hardness, strength, toughness and so on. Generally speaking, the wear resistance of the alloy with higher hardness is relatively good, but the toughness is often lower ; the alloy with good toughness is more suitable for the condition of impact load. In addition, the cost factor is also an important aspect to be weighed in the selection process. Due to the great difference in price between cemented carbides with different compositions and properties, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the cost under the premise of meeting the requirements of use to achieve greater cost performance.
The difference between cemented carbide and ordinary steel
Compared with ordinary steel, the advantages of cemented carbide are particularly obvious. Generally speaking, the hardness of ordinary steel is in the range of HRC20 to 60, while the hardness of cemented carbide can reach HRA89 to 93, which is much harder than that of ordinary steel. In addition to wear resistance, in such as high-speed cutting, heavy-duty cutting this more stringent, laborious working conditions, cemented carbide wear much slower than ordinary steel, can maintain a good cutting effect for a long time. There is also heat resistance. The performance of cemented carbide is very stable at high temperature and will not change much. However, once the ordinary steel encounters high temperature, the hardness and strength will decrease significantly, and there is no way to meet the requirements of high temperature work.